AI Ethics in Education: Balancing Innovation with Responsibility
The discussion surrounding AI ethics dates back more than 70 years, with Isaac Asimov introducing the “three laws of robotics.” AI ethics is a critical issue that influences many industries. According to research, at least 9 out of 10 businesses encounter ethical issues created by AI (Denison, 2023). But what about the educational sector? Ethical challenges such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and accountability are a part of grading systems, classrooms, and student support. It is important to address these concerns to ensure that the use of AI in education is fair, transparent, and meets ethical norms. One of the examples of the successful use of AI in education based on ethical principles is EduLegit – the platform developed for students and teachers for writing process monitoring, transparency, accountability, and privacy.
What are AI ethics?
AI ethics is a set of governing principles and recommendations that can be used to solve ambiguous situations (Denison, 2023). Business and government organizations apply those guidelines to form AI policies. As such, AI ethics is necessary to minimize risks and guarantee the best results when using AI-based tools and solutions. AI ethical principles are critical for an educational system that adapts to the use of technology.
Several studies have been conducted to determine the extent to which AI is currently used by students and teachers in managing everyday tasks. Interestingly, more than 80% of students already use AI in an unethical way to generate drafts or complete full assignments (Dakakni & Safa, 2023). It should also be pointed out that educators and learners have their concerns about AI in terms of, for instance, privacy concerns. In fact, teachers show a high level of readiness to undergo training for AI and be able to monitor students’ potential misuse of it. EduLegit is the tool to achieve this goal and ensure that students adhere to ethical norms.
5 Key Principles of AI Ethics in EduLegit
EduLegit incorporates five key principles of AI ethics to ensure its customers approach assignments responsibly and fairly, promoting trust and safety in educational technology.
Transparency
At EduLegit, transparency is foundational. We believe educators, students, and administrators need to understand how our AI systems work and why specific decisions—such as grades or feedback—are made. The system develops a report for each task with data that analyzes a text and includes all relevant features. Such reports can be used for learning from mistakes and fair grading.
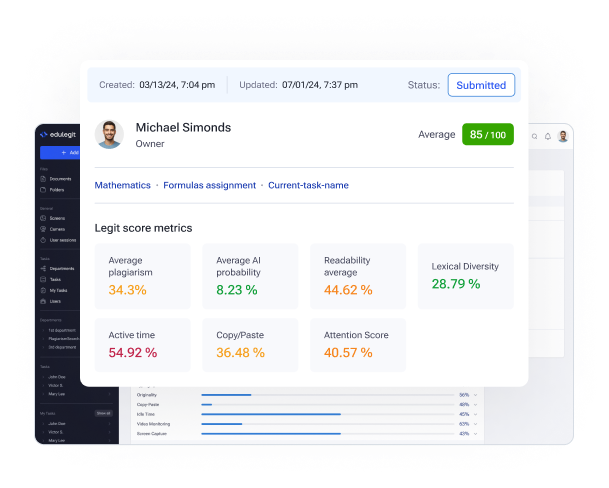
For example, our EduLegit score retrieves data on a student’s work and considers such criteria as average plagiarism rate in papers, readability of the student’s texts, lexical diversity and academic language the student uses in their writing, active time spent on assignments, attention patterns, and typing and copy-pasting behaviors. All those metrics are based on certain AI algorithmі that analyze student involvement and effort put into work. Therefore, the EduLegit score ensures that educators have sufficient data and reason to make an informed decision and grade students adequately all while maintaining control over the learning process and outcomes.
Fairness
To ensure impartiality, our AI is trained on large datasets that help better understand learning styles, skills, approaches to writing, and more. Most importantly, AI is trained to decrease bias and ensure equality. Ensuring that AI systems use diverse datasets is essential to promote fairness. Without this approach, AI might misinterpret some learning challenges students with different cultural or socio-economic backgrounds face.
Accountability
EduLegit embraces accountability at every stage of AI implementation. The teams behind EduLegit take responsibility for ensuring the AI’s outputs are accurate, fair, and explainable. In cases where human review is needed, educators are always in control, ensuring that any discrepancies or errors are caught and corrected. By fostering accountability, the AI tool remains a reliable option for teachers and students.
Reliability
Whether assessing student performance, grading assignments, or providing feedback, EduLegit ensures that its AI consistently produces accurate results. The platform ensures its algorithms perform effectively across different use cases and educational environments through continuous monitoring and updates. To maintain reliability, EduLegit implements regular performance checks and error reporting systems. Educators and students are also encouraged to report any irregularities, allowing the team to address issues swiftly and refine the AI to meet evolving educational needs.
Security and Privacy
We prioritize data security and privacy. We do not gather or share any information with third parties. Data is processed securely, and students’ personal information is never used for purposes beyond what is necessary for educational support. EduLegit also ensures that only authorized users can access student data (notably, teachers). By maintaining high-security standards, an AI system can adhere to the principle of privacy.
While AI in education presents challenges for students and teachers regarding its trustworthiness and reliability, it is possible to use AI tools and adhere to ethical norms. EduLegit shows how AI can balance the use of technology without compromising privacy and fairness. The platform recognizes the possible practical usage of AI, takes accountability, and creates an environment that promotes authenticity. We also address privacy concerns and prevent bias to ensure that AI is used responsibly.
Sources Used:
Denison, G. (2023). What are AI ethics? 5 principles explained. Prolific. https://www.prolific.com/resources/what-are-ai-ethics-5-principles-explained.
Dakakni, D. & Safa, N. (2023). Artificial intelligence in the L2 classroom: Implications and challenges on ethics and equity in higher education: A 21st century Pandora’s box. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, vol. 5, 2023, 100179.


Can AI Assess Essay Samples Fairly?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a technological breakthrough across various spheres, including education. Yet, its role is still uncertain for people […]

AI in Education: EduLegit’s Role in Shaping Honest Digital Learning
The search for optimizing the educational process and making studies more engaging and effective for students and educators allowed AI […]

AI Ethics in Education: Balancing Innovation with Responsibility
The discussion surrounding AI ethics dates back more than 70 years, with Isaac Asimov introducing the “three laws of robotics.” […]